📘 Chapter Title: Commercial Rooftop Unit (RTU)
📄 Rooftop Unit (RTU)Description:
Overview
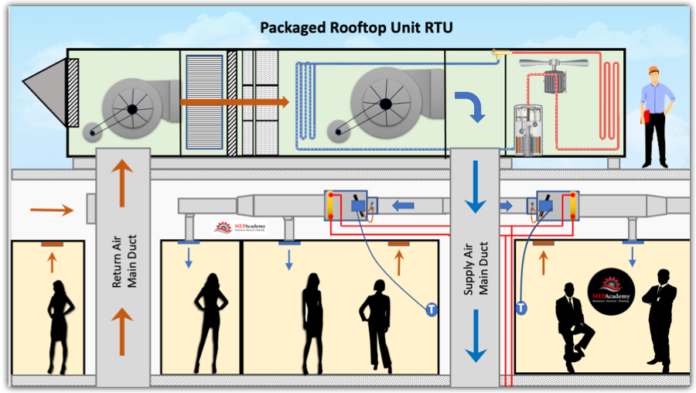
This chapter covers the key functions, components, and applications of ACommercial Rooftop UnitUnits (RTU)RTUs) is a —self-contained HVAC system typicallysystems installed on the roof of commercial and industrial buildings. It provides heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) by drawing outdoor air, conditioning it (heating or cooling), and then delivering the treated air into the building viarooftops. ductwork.
RTUs are packagedwidely units,used meaningin allcommercial majorsettings components—compressor,like condenser,retail evaporator,stores, blower, filters,offices, and controlschools systems—aredue housedto intheir acompact single cabinet. This makes installationfootprint and maintenanceall-in-one moreheating, convenientcooling, comparedand toventilation split systems.design.
Readers
Keywill Components
learn:
-
Compressor:HowCompressesRTUsrefrigerantoperatetoandfacilitatedistributeheatconditionedtransfer.air -
CondenserKeyCoilcomponents:& Fan:Releasescompressors, heatfromexchangers,thesupply/exhaustrefrigerantfans,to the outside air.economizers -
EvaporatorTypicalCoil:capacities,Absorbsvoltages,heatandfromairflowreturn air to cool the building.configurations -
Blower/Fan:CurbCirculatesinstallationconditioned air into the buildingrequirements anddrawscranein return air.considerations -
Burner or Electric Heat Elements:Provides heating in gas/electric or electric-only models. Filters:Clean the air before it is circulated indoors.Dampers:Regulate outdoor air intake for ventilation or economizer function.Control System:Manages temperature setpoints, fan speeds,Maintenance andeconomizerservicelogic.access best practices
RTU
Types
Figure: Diagram ofRTUswith
- airflow
Cooling-Only RTUs:Provide only air conditioning; common in warm climates.
Gas/Electric RTUs:Use natural gas for heatingpath andelectricitykeyforinternalcooling.components
Heat Pump RTUs: Use refrigerant to both heat and cool via reversing valve.
Multizone RTUs: Serve multiple areas of a building with individual temperature control.
Applications
RTUs are commonly used in:
Office buildingsRetail storesWarehousesSchoolsRestaurants
They are preferredDesigned for theirtechnicians, compactAPMs, footprint,and easefacility teams, this chapter includes visuals, example models, and links to video walkthroughs of access, and cost-effective installation, particularly where rooftop space is available and noise concerns are minimal.
Advantages
serviceAll-in-one design simplifiesRTU installation andservicing.procedures. - It’s
Saves interior space by mounting equipment on the roof.
fieldEconomizers can reduce energy consumption by using outdoor airideal forcooling.Modular capacity makes them scalable for larger buildings.
Limitations
Limited to buildings with flat or low-slope roofs.More exposed to weather, requiring proper sealingreference andmaintenance.onboarding new team members.Noise and vibration can transfer into the building if not properly isolated.
Maintenance Considerations
Regular inspections are critical to RTU performance:
Filter changes(monthly or quarterly)Coil cleaningto maintain heat transfer efficiencyBelt and motor inspectionsControls and sensors calibrationDrain pan and condensate line cleaning
Related Equipment
Split HVAC SystemsAir Handling Units (AHUs)Variable Air Volume (VAV) SystemsPackaged Terminal Air Conditioners (PTACs)