Commercial Rooftop Unit (RTU)
This
📘 chapter covers the key functions, components, and applications of Commercial Rooftop UnitsUnit (RTUs)RTU) Overview
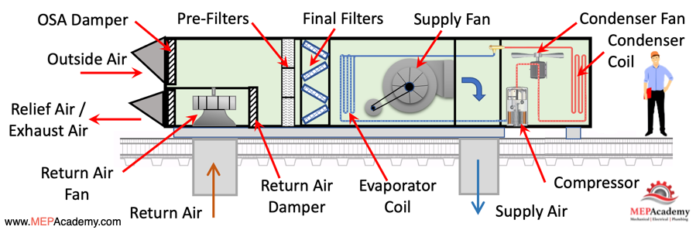
📷 RTU System Diagram
Figure 1: Basic RTU layout showing supply/return air, compressors, and heat exchangers.
🧰 What is a Rooftop Unit?
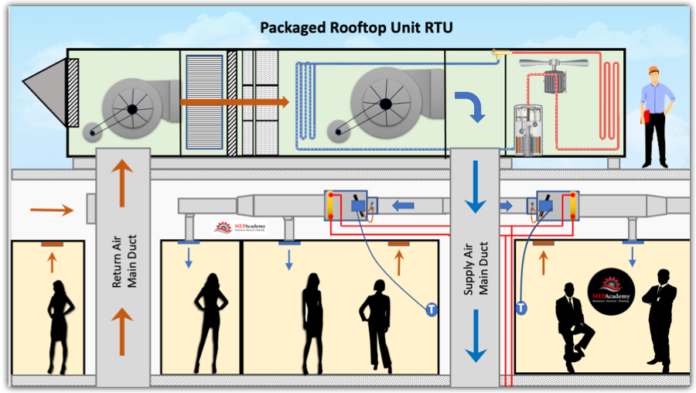
A Rooftop Unit (RTU)—self-contained is a packaged HVAC systemssystem installed on buildingthe rooftops.roof RTUsof are widely used ina commercial settingsbuilding. likeIt retail stores, offices, and schools due to their compact footprint and all-in-onecombines heating, cooling, ventilation, and ventilationair design.distribution into a single cabinet, making it ideal for spaces that lack mechanical rooms.
ReadersRTUs willcondition learn:air and deliver it through ductwork connected from the roof to interior zones.
Used in:
-
HowRetailRTUs operate and distribute conditioned airstores -
Key components: compressors, heat exchangers, supply/exhaust fans, economizersSchools -
TypicalOfficecapacities, voltages, and airflow configurationsbuildings -
Curb installation requirementsGyms andcrane considerationswarehouses
🔧 Key Components
🔹 Cabinet
-
MaintenanceWeatherproof housing for all major components
🔹 Supply & Return Fans
-
Drive airflow through the building’s ductwork
🔹 Compressor & Refrigeration Circuit
-
Provides cooling via a refrigerant cycle
🔹 Gas Furnace or Electric Heat Section
-
Provides space heating
🔹 Economizer (Optional)
-
Allows use of outside air for “free cooling”
🔹 Filters & Dampers
-
Clean air and
servicecontrolaccess best practicesintake/exhaust
Figure:FigureDiagram of2: RTUwithmaintenanceairflow path and key internal componentsaccess.
📏 Typical Specs
-
DesignedTonnage Range: 3 to 60 tons -
Voltage: 208/230V, 460V 3-phase
-
Mounting: Roof curb or rail
-
Airflow: Side or bottom discharge/return
🧱 Installation Considerations
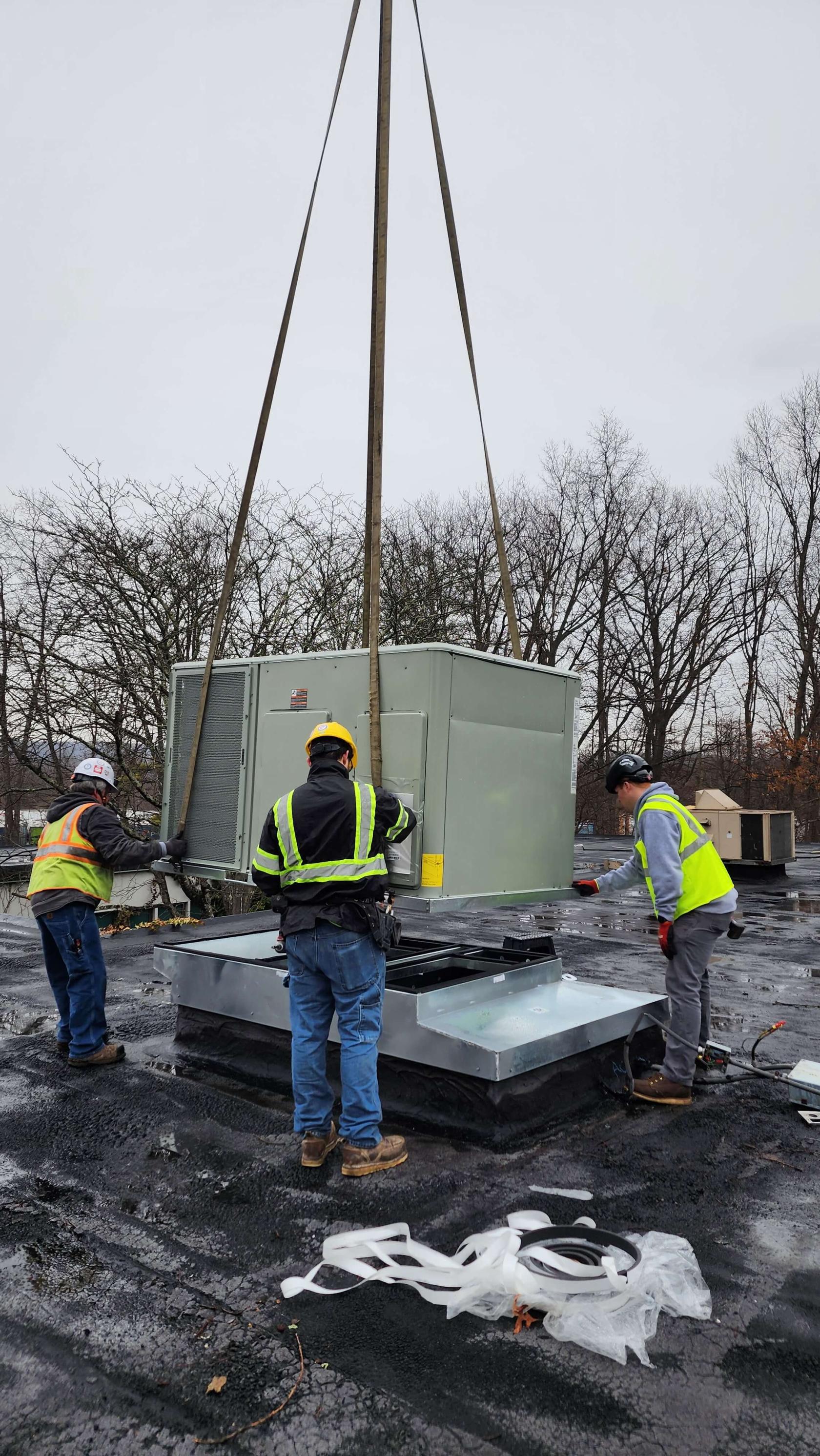
Figure 3: RTU being installed on curb via crane lift.
-
Requires roof curb and structural reinforcement
-
Duct cutouts must match RTU supply/return layout
-
Condensate drain and electrical connections needed
-
Consider local code compliance (curb height, seismic, clearance)
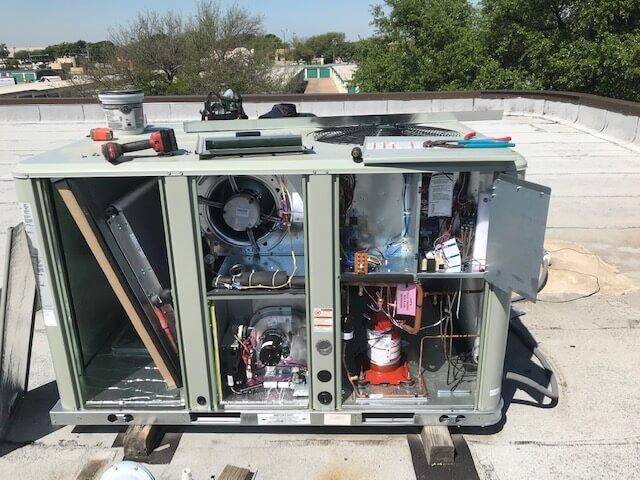
🧼 Maintenance Requirements
Figure 4: Service panel access fortechnicians,quickAPMs,maintenance.and
facilityteams,
✅ includesAdvantages
-
models,All-in-one
andsolutionlinks(heat, cool, ventilate) -
Saves indoor mechanical room space
-
Easy access for service via roof
-
Works well with zone VAV systems
⚠️ Disadvantages
-
Requires crane for installation
-
Exposed to
videoweather—mustwalkthroughsbeofmaintainedRTU -
andLarge
serviceunitsprocedures.mayIt’srequire roof reinforcement -
Not ideal for
fieldmultistoryreferenceduct risers
🛠️ Common Issues
-
Tripped high-pressure switch
-
Dirty condenser coil reducing efficiency
-
Worn fan belts causing poor airflow
-
Economizer failure (stuck damper or sensor fault)
📎 Training & Resources
🧠 Summary
RTUs are versatile, self-contained HVAC systems ideal for commercial buildings needing reliable, rooftop-mounted climate control. They simplify installation, reduce mechanical room needs, and onboardingare newaccessible teamfor members.service—making them a go-to option for many HVAC designs.